EU Airport Slots

An increasing number of airports require slots worldwide and especially in Europe. While airport coordination and slot regulation are officially considered an “interim solution to manage congested infrastructure until the longer-term solution of expanding airport capacity is implemented,” the slots are here to stay, along with the increased traffic volumes and limited capacities. Check your general slot knowledge with the following brief overview.
What is an Airport Slot?
An airport slot allows the operator to operate to an airport at certain, specified times. Airport slots are in use at airports that are constrained due to runway capacity and/or parking space – in other words, where the demand exceeds the airport infrastructural capacity.
Note: Airport slots are different from airway slots. Airway slots are designed to manage airway capacity. Airway slots are assigned and monitored in Europe by Eurocontrol Network Manager.
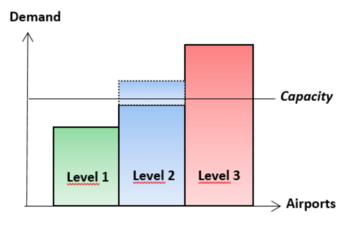
What is a Coordinated Airport?
Airports are classified into three different categories according to the level of congestion:
Level 1 – Airport capacity is generally adequate to meet the demand at all times. No coordination is required and no slot procedures apply.
Level 2 – Airport capacity has the potential for congestion during some period of the day/week/season which can be resolved by mutually agreed schedule adjustments. A facilitator is appointed to facilitate the planned operations. Flight schedule notification is required and the facilitator may offer alternative operating times to avoid exceeding the parameters. Slot request procedures may apply for Business and General Aviation operators.
Level 3 – Airport capacity is regularly exceeded by demand. A coordinator is appointed to allocate slots to airlines and operators to manage the airport capacity and to maximize the efficient use of the airport’s infrastructure. Slot request procedures apply.
Who Regulates and Assigns Airport Slots?
Airport slots are managed by the slot coordination bodies that are appointed on a country basis by the responsible authorities following consultations with the airport, airline, and representative organizations (e.g. IATA). The European Airport Coordinators Association groups airport coordinators from the EU’s 28 member states.
Who Sets the Standards for Slot Coordination?
The worldwide slot management standards are set by the International Air Transport Association (IATA) in the Worldwide Slot Guidelines (WSG). IATA WSG is a set of standards developed by the IATA Member airlines together with the airport coordinator and facilitator communities. The IATA WSG is recognized by the global air transport community as the industry standard methodology for the allocation of slots and management of planned operations. Along with the IATA WSG, the IATA Standard Schedules Information Manual (SSIM) provides a set of recommended practices, messaging formats, and data processing procedures for communication and efficient exchange of airport coordination information.
How Many Airports are Coordinated in Europe?
Europe currently includes 180 coordinated (Level 3) and schedule facilitated (Level 2) airports. Certain airports experience seasonal variations following summer/winter destination trends. The summer season is significantly busier with 104 coordinated airports, while this number drops to 76 in winter season. Popular airports on the Mediterranean islands (e.g. Greek islands, Ibiza, Menorca, Olbia) require slots during the summer season.
Who Can Request a Slot?
In general, Business and General Aviation operators can choose to either request the slots directly or ask their handling agent to manage the slots. However, certain countries mandate only authorized representatives (i.e. handling agents) process slot requests for all private flights. These countries include Belgium, France, Greece, and Switzerland. On the contrary, handlers in Iceland and Greenland encourage the aircraft operators to request slots directly from the Nordic Airport Coordination.
How to Request a Slot?
Business and General Aviation operators request slots using the General Aviation Slot Clearance Request GCR (GCR) format. The GCR format was developed due to increased demand for airport slots for private flights and is a somewhat different and simplified version of the Slot Clearance Request (SCR) format used by airlines. The main difference between the GCR and SCR format is the airport codes: GCR format uses ICAO codes, while SCR format is based on IATA codes. GCR format is internationally recognized and referenced in the IATA Standard Schedules Information Manual (SSIM), appendix K. Guidance material for the GCR format is available on several slot coordination websites.
Sources



